How to choose an authentic EVOO

Posted On: Jan 29, 2022
Categories: Learn
Tags: quality , science , olive grove , biodiversity , harvest , terroir , climate , olive mill
A guide to help you choose the right olive oil for you based on taste, quality and health benefits
Olive oil is a wonderful ingredient with astounding versatility in the kitchen. Yes, olive oil is more than the perfect ingredient for salad dressings. You can cook a wide variety of foods with it, and you can bake with olive oil as well!
There’s no doubt the super-healthy oil everyone’s talking about has a place in the kitchen. But not olive oils are made in the same way, and they’re not all the same quality.
Here’s what you need to know about olive oil, including a comparison between extra virgin vs simple olive oil. After reading this, you’ll have the knowledge to buy the right type of olive oil for you, avoid scams and counterfeits, and cook with olive oil. This is our ultimate guide about types of olive oil. All the secrets revealed.
Different Categories of Olive Oil
All olive oil comes from olives, most commonly grown around the Mediterranean Basin. And although there are around 4 million hectares dedicated to the noble crop, not all of them are destined to produce the prized extra virgin olive oil.
In the European Union, there are several categories of olive oil. The first four categories comprise refined oil with little to no aroma, more often than not destined for industrial purposes:
- Lampante
- Refined Olive Oil
- Crude Olive-Pomace Oil
- Refined Olive-Pomace oil
The quality begins after the four categories above, with prestigious oils including:
- Virgin Olive Oil
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO).
These are amongst the most prized cooking oils in the world and shine for their organoleptic properties and low acidic levels. Virgin olive oil has less quality than EVOO, of course, but it has its uses. Virgin olive oil can have a maximum 2% acidity and certain defects of scent and flavor. Extra virgin olive oil has a maximum acidity of 0.8%.
Some of the most pleasing virgin and extra virgin olive oils are also protected by appellations of origin or PDOs, which may indicate a pristine provenance.
What Is Premium Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
The term ‘premium’ is not regulated by the European Union, but it always refers to the highest quality extra virgin olive oils. Although the term ‘premium’ can be abused, it is often used to describe the finest olive oil; olive oil that takes you places with a unique personality that reflects the land with a polished sense of place, or what the French call “terroir.”
Premium olive oil is easy to distinguish when compared to simple olive oil. It will offer endless layers of flavor and the most exquisite mouthfeel. Of course, although every producer can make extra virgin olive oil, only the most dedicated oil producers can craft a premium product.
What to look for in authentic olive oil bottles?
The European Union has set in place strict rules and norms to guarantee virgin and extra virgin olive oil’s quality. They’ll perform controls and take samples during the entire production process and provide regulations for packaging and labeling. And although the market for authentic extra virgin olive oil is living a golden era, a shadier, counterfeit market exists.
Be Careful of Counterfeits!
- Olive oil not labeled as “extra virgin” should generally be avoided.
- Virgin is of lower quality than extra virgin. It has few health benefits, high acidity and taste defects.
- Oil labeled as “Blended” olive oil might contain grain or vegetable oil.
- Third-party certifications, such as recent awards from olive oil competitions are often good indicators.
- Fake extra virgin olive oil is easy to spot on the nose and palate, as it lacks the complexity and the aromas of the real deal.
- Buying olive oil straight from acknowledged producers you trust or shops that bring high quality olive oils.
This last step is very important, because the important information about the quality is not found on olive oil labels. Establishing a direct contact with the producers or your suppliers is important to learn more about the producer's practices.
Note: Countries outside the European Union can produce olive oil of superb quality, although their labels will lack the transparency and reliability of European versions. Trust ‘new world’ olive oil only if it comes from respected producers.
Factors of Quality in Olive Oil
What makes extra virgin olive oil great? Many factors come together for an authentic delicacy and culinary experience. These are just a few factors that influence olive oil’s quality.
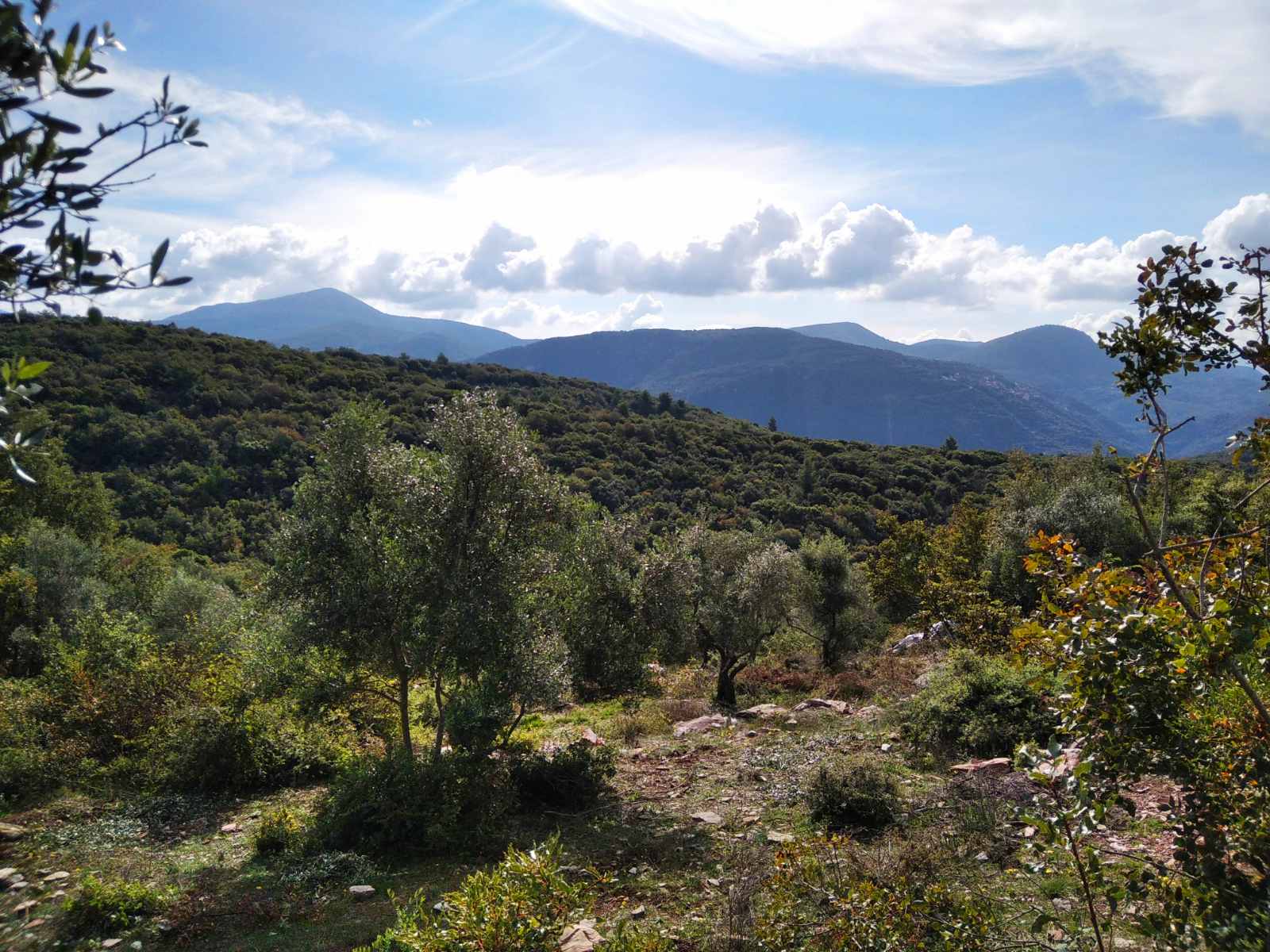
Natural Conditions and Olive Grove
Similarly to wine, the most important aspect about the character of the olive oil is what the french call "terroir". Terroir can be defined as an interactive cultivated ecosystem, in a given place, including climate, soil and the olive grove. Olive oil sensory attributes are influenced by the terroir, in such a way that olive oil from the same variety of trees cultivated under different conditions may a have a totally different taste. Needless to say that intensive farming in exhausted flat land groves gives poorer quality oil comparing to high altitude slopes , with rocky biodiverse terrain. Only to name a few parameters that define a good terroir.
- High altitude and slightly colder climate helps to preserves antioxidants and vitamins.
- Selected rocky mountainous slopes offer ideal drying and natural ventilation.
- Specific olives are more suitable for oil production, while others are best enjoyed as food. The varietal used has a significant impact on olive oil’s quality.
- Maintaining a biodiverse terrain. Frequent use of herbicides, pesticides, fertilisers weakens the diverse network of micro-organisms in the rhizosphere of the plants, causing the loss of the balance of the biological system of the tree.
Applying the best agricultural practices
We have to keep in mind that olive oil is a juice full of vitamins and antioxidants. In order to obtain a tasty olive oil, we need great quality olive fruit. Therefore applying following modern agricultural practices to achieve top-quality olive fruit is important.
- Only high quality olives without bruises and black spots will make a great juice and keep the acidity levels low.
- The olives should be harvested at the right time. Late harvest may affect negatively the intensity and amount of antioxidants in the olive fruit.
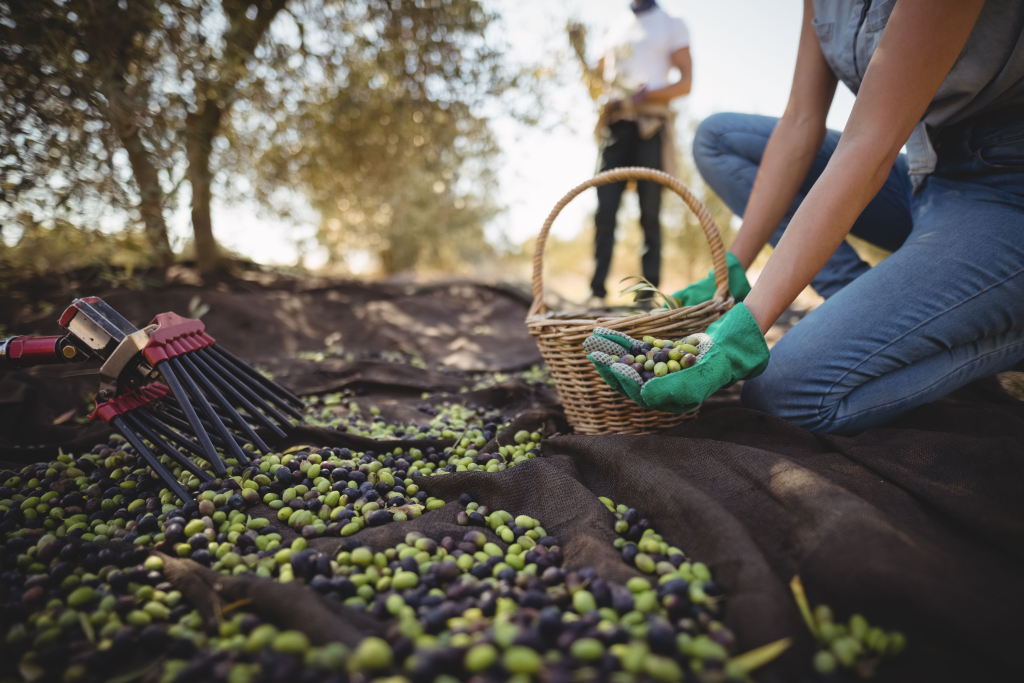
- The harvest conditions are of paramount importance. The extraction should take place within a few hours after the harvest to avoid damaging the olives.
- High temperatures may destroy the taste. Using plastic bags or leaving the harvest under the sun for a long time, may raise the temperature and result in higher acidity.
- Harvesting olives is one of the most laborious and time-consuming processes in agriculture. Certain mechanical harvesting might make the process faster and less expensive, but it might take a toll on the fruit’s quality. Traditional harvesting or using light mechanical methods is always better.
- The experience of the olive oil makers plays a significant role in the quality of the oil. Some estates go back for generations and have mastered the art of making premium olive oil for decades and sometimes centuries. You can tell if a producer is knowledgable often from showing consistency in wining awards in global olive oil competitions
Conditions at the olive mill
Quality olive oil is cold-extracted from fresh olives, and it’s never refined or contaminated with chemicals, additives or heat-extracting methods. The extraction method is a pure mechanical process. Often the olive mills are in tight schedule and apply high speeds and high temperatures to finish on time, to a detriment of the quality. The following practices should be applied so as to receive the fresh oilve oil juice as pure as possible.
- Extraction should take place within a few hours after harvest
- Organoleptic analysis should be performed right after extraction, before and after bottling to ensure that there are no defects in taste.
- Short-time malaxation should be applied.
- Low temperatures should be used during the extraction. High temperatures can damage the taste and aromas.
Are all Extra Virgin Oils of the Same Quality?
Although extra virgin olive oil represents the highest quality tier for olive oil, they’re not all the same quality. Some olive oils, more often than not produced by large corporations, might have flaws and defects. Large companies often blend different olive oil to get larger yields. The best olive oils often comes from single estates.
To learn more about what factors influence olive oil’s quality, we invite you to explore The International Olive Council (IOC) trade standards.
What’s the Right Olive Oil For You?
Now that you know that not all olive oil is the same and that there are differences even amongst the revered extra virgin olive oils, it’s time to find the right olive oil for you. There’s olive oil for every palate and budget, and we all have our favorites. When choosing a bottle of olive oil, think of the farmers, be mindful of the oil’s provenance and history.
Every bottle of olive oil tells a story, and it’s those stories that make it so special. Find your favorite olive oil producer and share its passion for the premium oil in your kitchen!